
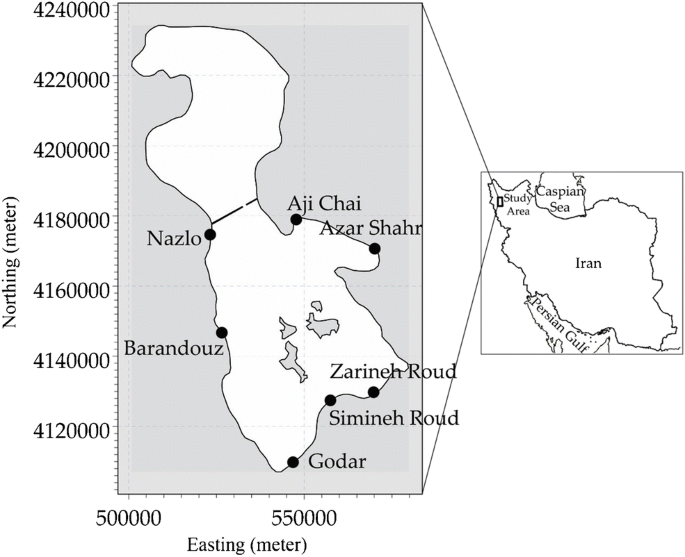
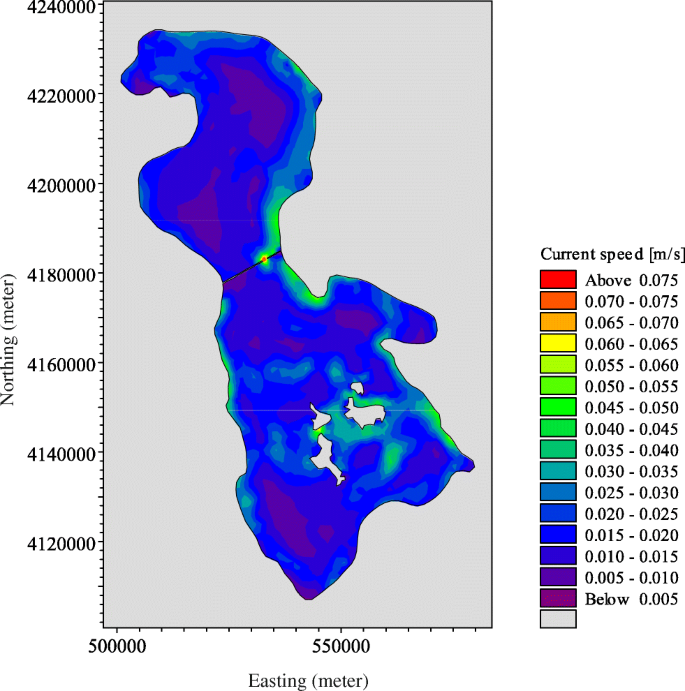
The novel method was applied in case studies to reconstruct real image data for the cerebral angioarchitecture. We demonstrate the reliability of our algorithm in terms of mesh quality by evaluating scaled Jacobian and equiangular skewness.
#3d visual of computational mesh mike 21 full
The methodology requires no user interaction, can create volumetric meshes for non-planar bifurcations and offers full control over the local mesh resolution at the surface and the lumen of the blood vessels. Our aim is to present a fully automatic algorithm for parametric mesh representation of vascular networks from subject-specific medical images. Current mesh generation methods require user interaction and cannot be used for automatic generation of parametric mesh representations of vascular networks.
However, structured parametric meshes can better represent complex geometries with lower grid density thus enabling faster and more precise computations. Unstructured meshes are widely used to delineate the complex geometry of blood vessels in computational fluid dynamics simulation. Linninger, in Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 2015 Abstract It also enables object-based retrieval of video objects by providing accurate object trajectory information and syntax for vertex-based object shape representation. Mesh modeling can efficiently represent continuous motion, resulting in less blocking artifacts at low bit rates as compared to the block-based modeling. Motion compensation is performed by spatially piecewise warping of the texture maps that correspond to the triangular patches. The vertices of the triangular mesh elements are called node points, and they can be used to track the motion of a video object, as depicted in Fig. In order to benefit from functionalities provided by such representations, MPEG-4 Part 2 supports two-dimensional (2D) and 3D mesh representations of natural and synthetic visual objects, and still texture objects, with triangular patches. Mesh representations have been successfully used in computer graphics for efficient modeling and rendering of 3D objects. Bezier surfaces and sweeping are the basic methods and ensure that the surface normal changes continuously.Ī mesh is a tessellation (partitioning) of an image into polygonal patches. They put emphasis on correctly representing branches and compose a vascular tree of tubular segments and a branching model that are smoothly blended. This method has been explicitly refined for using it in catheterization training. One method that we briefly introduced in Chapter 11 is based on sweeping and implicitly reconstructs vascular models. Similarly good results may be achieved with subdivision surfaces. However, even better quality is possible with more recent surface modeling techniques, which perform polygonization in an adaptive manner, creating a high resolution only in highly curved areas. Other implicit surface representations are more accurate and exhibit a better triangle quality, e.g., the modified MPU implicits (recall § 11.6.2 and Schumann et al. Ĭonvolution surfaces avoid these problems but require a remeshing step to ensure a sufficient triangle quality. Even the best explicit surface reconstruction, e.g., based on truncated cones, cannot avoid internal polygons and exhibits discontinuities at branchings. Here, we discuss which of them fulfills the set of requirements stated above. Selection of a Modeling Technique In Chapter 11, we introduced a number of vascular surface modeling techniques. These additional requirements are very similar to those of blood flow simulation where the surface mesh also serves as input for volume mesh generation (§ 19.3.2). Moreover, it should be appropriate for a fast and numerically stable simulation, that is, the triangle quality needs to be high (degenerated triangles with very small angles need to be avoided) and the geometric complexity should be low. These requirements are the same as those for virtual angioscopy an endoscopic procedure to move a camera through vasculature (recall § 13.6.3). Requirements The vascular surface mesh representation should be smooth and accurate and should not contain any internal structures that would hamper the movement of a catheter. Bernhard Preim, Charl Botha, in Visual Computing for Medicine (Second Edition), 2014 21.6.5.2 Vascular ModelingĪn essential prerequisite for the simulation is an appropriate surface mesh representing the relevant part of a vascular system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
